Threat intelligence feeds
Feeds contain indicators that can be automatically imported in MISP at regular intervals, they can be both remote or local resources. Such indicators contain a pattern that can be used to detect suspicious or malicious cyber activity.
Feeds can be structured in three different formats:
MISP standardized format which is the preferred format to benefit from all the MISP functionalities
CSV format, allows you to select the columns that are to be imported
Free-text format allows automatic ingestion and detection of indicator/attribute by parsing any unstructured text
You can easily import any remote or local URL to store them in your MISP instance. Feeds description can be also easily shared among different MISP instances as you can export a feed description as JSON and import it back in another MISP instance.
Adding Feeds:
Hover the cursor over Sync Actions from the main navigation barand select List Feeds. The default feeds and the current version of MISP are displayed on this page.
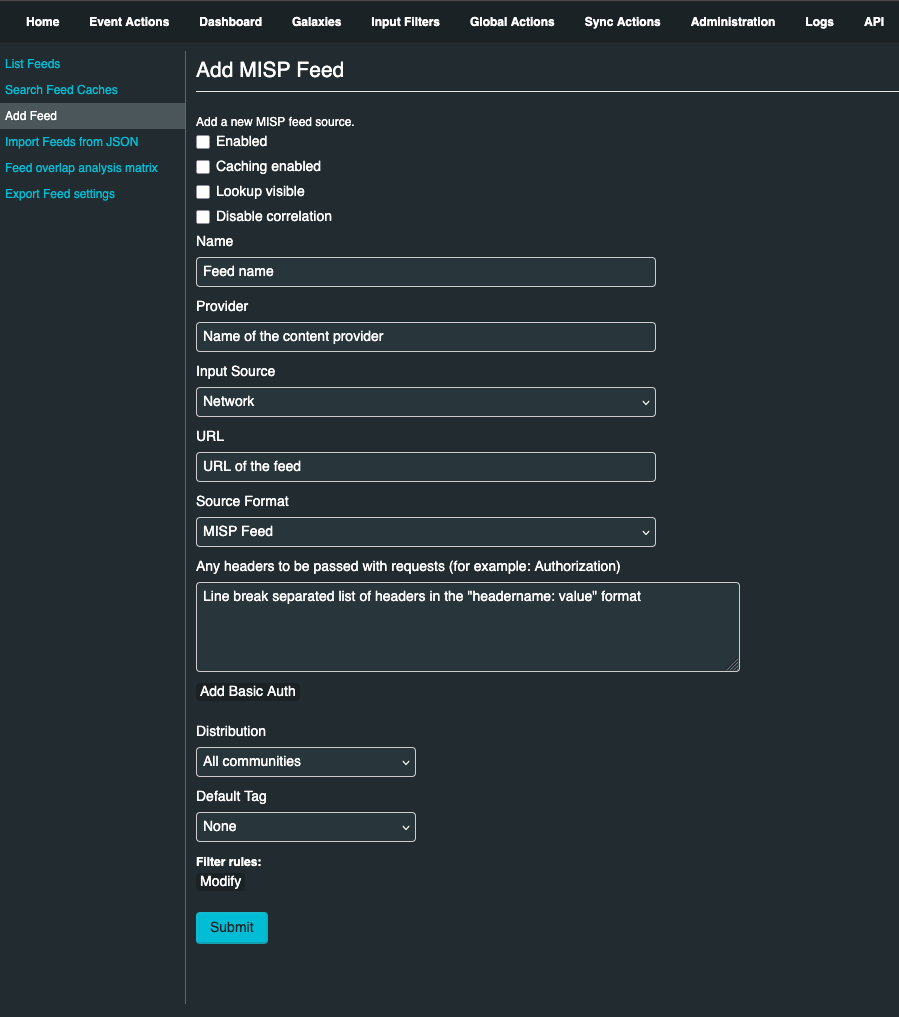
On the left pane, click Add Feed to open the Add MISP Feed page. You will need to provide the following details:
Enabled: Is the feed active or not
Lookup visible: If this is not checked, the correlation will only show up to you, if checked, correlations are visible for other users as well
Caching enabled: To enable a feed for caching, you need to check the caching enabled field to benefit automatically of the feeds in your local MISP instance
Name: It is a name to identify the feed
Provider: It is the name of the content provider
Input Source: Drop-down from Input Source menu and select either:
Network: hosted somewhere outside the platform
Local: Hosted on the local server. Once this option is selected, another checkbox Remove input after ingestion will appear. Tick this checkbox if you want to be deleted after the usage.
URL: URL of the feed, where it is located (for Local hosted files, point to the manifest.json e.g. /home/user/feed-generator/output/manifest.json)
Source Format: Drop-down from Source Format menu and select either:
MISP Feed: The source points to a list of json formatted like MISP events
Freetext Parsed Feed:
Target Event: These are the event that get updated with the data from the feed. Target Event can be either New Event Each Pull (A new event will be created each time the feed is pulled) or Fixed Event (A unique event will be updated with the new data. This event is determined by the next field)
Target Event ID: The ID of the event where the data will be added (if not set, the field will be set the first time the feed is fetched)
Exclusion Regex: Add a regex pattern for detecting iocs that should be skipped (this can be useful to exclude any references to the actual report / feed for example)
Auto Publish: If checked, events created from the feed will be automatically published
Override IDS Flag: If checked, the IDS flag will be set to false
Delta Merge: If checked, only data coming from the last fetch are kept, the old ones are deleted
Simple CSV Parsed Feed:
Target Event: These are the event that get updated with the data from the feed. Target Event can be either New Event Each Pull (A new event will be created each time the feed is pulled) or Fixed Event (A unique event will be updated with the new data. This event is determined by the next field)
Target Event ID: The ID of the event where the data will be added (if not set, the field will be set the first time the feed is fetched)
Exclusion Regex: Add a regex pattern for detecting iocs that should be skipped (this can be useful to exclude any references to the actual report / feed for example)
Auto Publish: If checked, events created from the feed will be automatically published
Override IDS Flag: If checked, the IDS flag will be set to false
Delta Merge: If checked, only data coming from the last fetch are kept, the old ones are deleted
Distribution: It define the distribution option that will be set on the event created by the feed
Default Tag: A default tag can be added to the created event
Filter rules: They allow you to define which organizations or tags allowed or blocked
Activating Publicly Accessible Feeds:
Click on “Sync Actions” at the top of the page and then Click “Feeds”
If you only see two lines listed under feeds, please Click “Load default feed metadata”
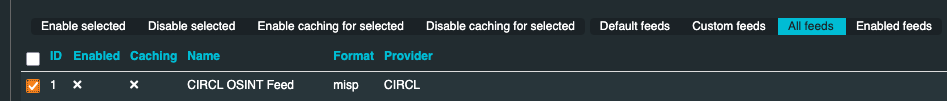
After performing step 2, you will have a list of 70 feeds that can be enabled. To do select the relevant check boxes for the feeds you want and then Click “Enable selected”, the page will refresh and the feed source will be enabled. If you would like caching enabled, Select the feed and then Click “Enable caching for selected”. It is recommended to enable caching for all enabled feeds.
🔖 NOTE: You can enable all feeds that you like, if you do enable a large number or all feeds it will provide you with a large amount of data that can be used to enrich observables in Incident Response
Once you have enabled the feeds you prefer, Click on “Fetch and store all feed data” for force pull the events stored in the feeds.

You can check the progress by Clicking “Administration” and then “Jobs” on the menu at the top
This will present you with a list of running jobs to retrieve events
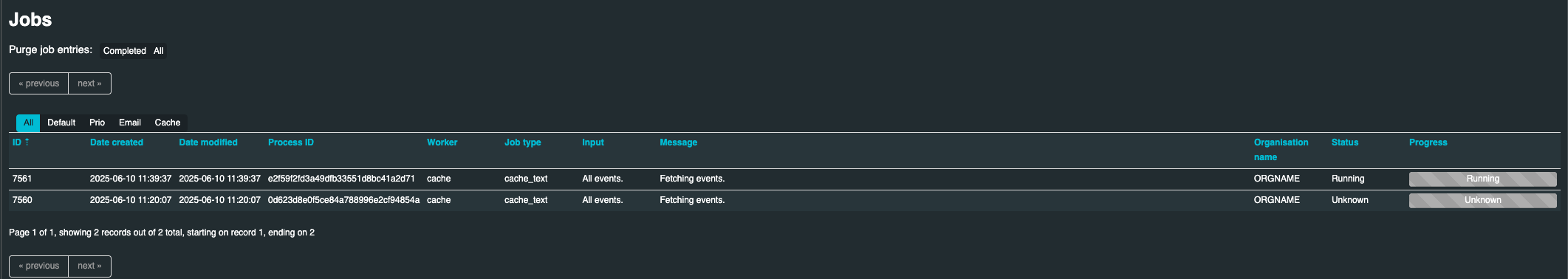
As the individual items complete, their progress will remain in this view with a status of “Completed”. To clean up the list, you can Click “Completed” next to “Purge job entries:”
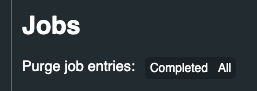
If you Clicked “All” it will remove all jobs, including those that are still running, you can trigger them again by performing “Step 4” again.
